Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: A Comparative Guide
Table of Contents
- Understanding what Cold Shrink Technology is
- Understanding what Heat Shrink Technology is
- Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: Comparison Overview
- Comparison of Installation Process
- Comparison of Performance and Reliability
- Cost Analysis: Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink
- Application Specifics: When to Use Cold Shrink vs Heat Shrink
- Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: Conclusion & Recommendations
- Frequently Asked Questions
Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: These are the two most popular methods used for Cable Connecting, Jointing, Tubing, Sleeving and Terminating as well as for other applications in various industries. Each method has its benefits and limitations. Thus, before making a decision on which to use, it is essential to consider all factors. These include costs, performance, installation requirements, safety considerations, environmental implications and more. This article explains the differences between cold-shrink and heat-shrink so you can choose the optimal solution for your project.
Historically, both Heat Shrink and Cold Shrink cable termination methods were pioneered in the 1960s alongside the rise of rubber and polyethylene insulated cables. This innovation introduced expandable materials that contract securely to protect cable joints, setting the foundation for modern reliable sealing solutions used across industries today.
Understanding what Cold Shrink Technology is
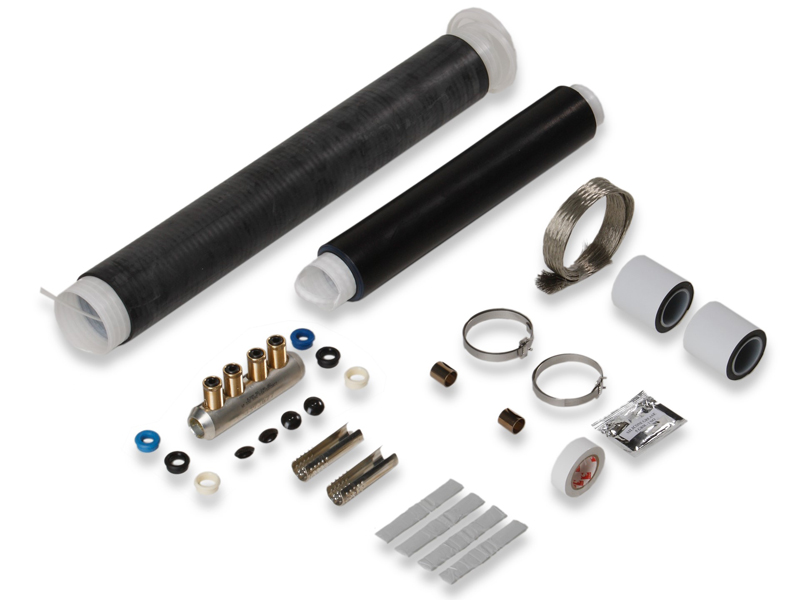

Cold Shrink Technology uses specially engineered elastomeric materials capable of expansion followed by natural retraction. It involves placing a pre-expanded tube/ sleeve with a supporting liner, over a connector or joint and releasing the liners. The joint, then, contracts and conforms tightly to the cable without the need for external heat.
This method offers several benefits, including ease of installation, increased safety, environmental friendliness and cost effectiveness. However, some limitations also exist, including limited material options as well as reduced chemical and mechanical resistance compared to Heat Shrink.
Understanding what Heat Shrink Technology is
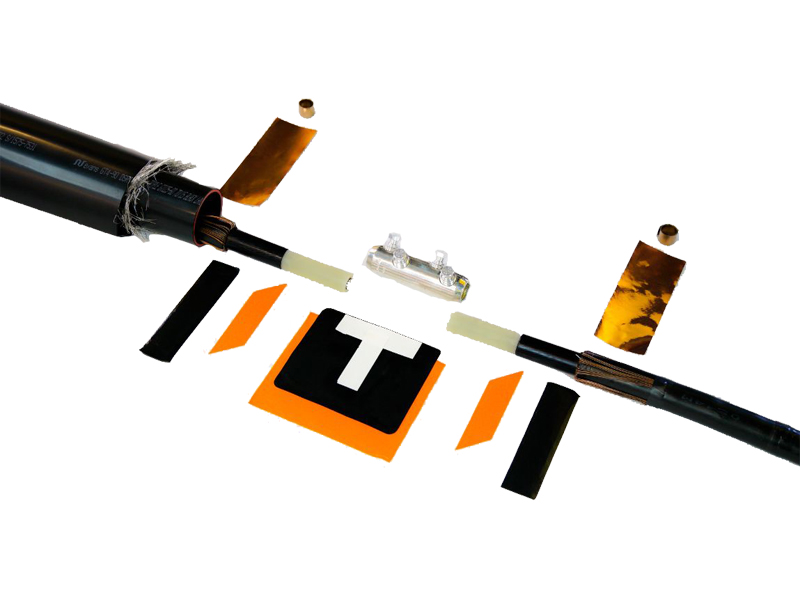
On the other hand, Heat Shrink Technology leverages thermoplastics whose molecular structure contracts when introduced to sufficient amounts of heat. To achieve this effect, users expose the heat shrink cable component to thermal energy with a blowtorch or heat gun. When reaching the necessary threshold, a reduction in volume takes place, creating a tight seal around the cable.
Key advantages of this approach include a wide range of available sizes, shapes and materials, each with specific properties suitable for different application. Another important benefit of this tight and strong seal is increased chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Some drawbacks compared to Cold Shrink, though, are the potential safety hazards of working with flames close to live wires, emission concerns, slower installation times as well as equipment and maintenance costs.
Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: Comparison Overview

Comparison of Installation Process
Installation Process of Cold Shrink

- Cold shrink products come pre-stretched on a supporting core/ liner.
- To install, the user must simply remove the supporting liner. This allows the product to shrink and form a tight seal around the application.
- No need for additional tools or heat sources during the installation process.
- The simplicity of the installation process makes cold shrink products fast to install even in tight spaces or challenging environments.
Installation Process of Heat Shrink
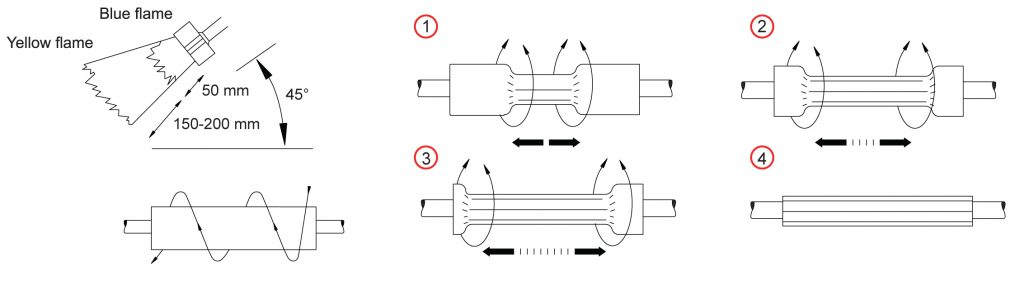
- Heat shrink cable products require the application of heat to shrink and form a seal.
- A heat source, such as a gas blowtorch, is necessary to shrink the tubing and create a secure connection.
- The user must ensure the proper amount of heat is applied evenly throughout the tubing to avoid over-shrinking or under-shrinking.
- The installation process of heat shrink cable products can be more time-consuming and require additional tools and installer expertise compared to cold shrink products.
Comparative Analysis
Cold shrink products offer an easier and quicker installation process that is tool-free and doesn’t require the application of heat. Heat shrink products, on the other hand, rely on heat for installation, which can be more labour-intensive and time-consuming.
Comparison of Performance and Reliability
When comparing the performance and reliability of heat shrink vs cold shrink methods, several factors need to be considered:
Cold Shrink Performance & Reliability
- Installation Process: Known for its quick and easy installation process that requires no heat source, reducing the risk of damaging sensitive components.
- Sealing Effectiveness: Provides excellent sealing properties due to its pre-stretched design that conforms perfectly to the application surface. It adjusts to cable expansions or contractions due to temperature changes.
- Temperature Range: Typically offers a wide temperature range, making it suitable for various environments, including extreme cold or drastic temperature changes.
- Long-Term Reliability: Cold shrink products are reliable and maintain their properties under normal environmental conditions, but may deteriorate over time if continuously exposed to chemicals, oils, etc.
- Application Versatility: Versatile and can be used in various applications, including telecommunications, rail, oil & gas and nuclear industries.

Heat Shrink Performance & Reliability
- Installation Process: Requires heat application using a gas blow torch or other devices, which may pose the risk of overheating and potentially damaging the material being covered. Also, a good final result requires a more experienced installer/ jointer.
- Sealing Effectiveness: While effective, the sealing properties and tightness depend on the application process and the skill of the installer. Big temperature decreases or long-term expansion and contraction can leave a void or create cracks between the cable and the seal. This allows moisture or contamination to get into the connection, causing damage.
- Temperature Range: The temperature range can vary depending on the type of heat shrink tubing used, with some variants performing better in specific temperature conditions. A wide range of options allow installers to choose the best solutions depending on the project.
- Long-Term Reliability: The long-term reliability may vary depending on the quality of the material and the installation process, with some heat shrink tubing more prone to degradation over time.
- Application Versatility: Widely used across different industries with a large range of different grade options available for different task profiles. The use of a blowtorch or heat gun can limit its versatility in some cases, making it difficult or impossible to obtain a permission in certain environments.
By considering these factors, individuals can make an informed decision based on the specific requirements of the project to determine whether cold shrink or heat shrink cable accessories are the most suitable option for their needs.
Cost Analysis: Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink
When it comes to a cost analysis between cold shrink and heat shrink options for cable insulation, several factors should be considered to determine the most economically viable choice:
- Material Cost: Heat shrink products have a typically lower initial cost compared to cold shrink tubes. However, additional accessories such as gas blow torches may be required when using heat shrink, adding to the overall expense.
- Installation Cost: Cold shrink products are popular for their easy and quick installation process, which can result in lower labour costs compared to heat shrink that requires time-consuming heat application.
- Equipment Cost: Heat shrink methods usually require special tools like heat guns or torches, which can add to the overall expense. In contrast, cold shrink systems do not require any additional equipment for installation.
- Maintenance Cost: Cold shrink products may deteriorate over time due to exposure to chemicals or mechanical tensions, leading to potential repair or replacement costs. The durability of Heat shrink products may lead to lower maintenance costs in the long run.
Considering these factors, the upfront cost of heat shrink may be lower, but installation and additional equipment may result in extra costs. Another factor to consider in this equation is the increased mechanical strength and chemical resistance of heat shrinks. This makes connections last longer and reduces replacement and maintenance costs.
Application Specifics: When to Use Cold Shrink vs Heat Shrink
When deciding between cold shrink and heat shrink technologies for your specific application, certain factors should be considered to determine which option is more suitable. Here are some key application specifics and environmental considerations to keep in mind:

Temperature Extremes
- Cold shrink products are known to perform better in cold environments or drastic temperature changes. This is possible due to its adjustment to the expansion or contraction of the cable. Therefore, in extremely cold or freezing temperatures, cold shrink may be the preferable choice to ensure a secure seal.
- Heat shrink products, on the other hand, require the application of heat to shrink and form a tight seal. This might be a challenge in very cold environments or those that require additional equipment to heat the tubing effectively. Extreme heat conditions, though, can make the seal even more rigid.
UV Exposure
- Cold shrink products tend to be resistant to UV exposure. This makes them a good choice for outdoor installations where the tubing is exposed to sunlight. This resistance helps maintain the integrity of the seal over time.
- Heat shrink cable tubing displays variable responses to UV exposure depending on their compound constituents. Some of them may degrade when exposed to UV rays over an extended period, potentially leading to a compromised seal. In such cases, additional UV protection options or coatings may be necessary.
Chemical Resistance
- Cold shrink products may be more susceptible to damage or degradation when in contact with certain chemicals. In such situations, heat shrink alternatives might offer better longevity and reliability.
- Heat shrink products are generally more chemically resistant than cold shrink products. They are more suitable for environments where exposure to oils, solvents or other chemicals is present.
Mechanical Strength
- Heat shrink products generally deliver greater mechanical stability since they become rigid upon activation, enhancing impact resistance and structural integrity.
- Cold shrink accessories aren’t as durable as heat shrink, but their capacity to accommodate movement is a great advantage. In other words, they retain a uniform distribution of compressive forces, featuring great mechanical strength when vibration, shock loads, drastic temperature changes or cyclic loading events take place.
Space Constraints
- In tight spaces or confined areas where using a gas blowtorch might be difficult or dangerous, cold shrink offers a more convenient solution as it does not require a heat source for installation.
Considering these factors will help you determine whether cold shrink or heat shrink technology is the most suitable solution for your specific application.
Heat Shrink vs Cold Shrink: Conclusion & Recommendations
Both cold shrink and heat shrink techniques have their advantages and disadvantages. Cold shrink is easier and quicker to install, making it ideal for installations in tight spaces or challenging conditions. On the other hand, heatshrink provides a more secure seal and is more suitable for applications where mechanical strength is a prerequisite.
Recommendations
- Consider the Application: Choose between cold shrink and heat shrink based on the specific requirements of your application. If quick and easy installation is a priority, opt for cold shrink. For applications that demand maximum protection and durability, heat shrink may be the better choice.
- Evaluate Environmental Factors: Take into account the environmental conditions where the installation will take place. If extreme heat is present, heat shrink may offer better long-term performance. Where big temperature changes or extremely cold conditions exist, cold shrink could be the best option.
- Installation Expertise: Cold shrink may be more user-friendly for beginners due to its simple installation process. For those with experience working with heat shrink, the additional steps involved may not be a deterrent.
- Cost Consideration: While cold shrink may have a higher initial cost, the savings in time and labour during installation could make it a cost-effective solution in the long run. Consider the overall project budget when making your decision.
In conclusion, the choice between heat shrink vs cold shrink ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the project. By evaluating factors such as ease of installation, environmental conditions, expertise, and cost, you can make an informed decision to ensure the success of your cable sealing and protection needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Cold Shrink and Heat Shrink Seals Actually Compare?
Heat shrink relies on adhesives and mastics to create a seal, which can degrade over time – especially as the cable expands and contracts with temperature changes. Since heat shrink material is rigid once cooled, it may not contract with the cable, leading to gaps that allow moisture and contaminants in. Over time, this can cause cracks, voids and eventual failure. Cold shrink maintains constant radial pressure around the cable, expanding and contracting as needed. Its flexible, elastic design ensures a consistently tight seal – without the risk of voids, adhesive failure or cracking.
Can Cold Shrink Reduce Electrical Tracking Issues?
Yes – cold shrink terminations made with silicone rubber offer excellent tracking resistance. Tracking occurs when voltage, moisture and contaminants combine to create a conductive path across the surface of an insulator, eventually leading to failure. Silicone’s natural hydrophobicity repels water and helps keep the surface dry, reducing leakage currents.
Why Should UV Resistance Be Considered When Choosing Between Cold Shrink and Heat Shrink?
Prolonged UV exposure can cause termination materials to degrade, leading to surface cracks that trap moisture and contaminants – conditions that significantly increase the risk of electrical tracking and failure. Silicone-based materials offer natural UV resistance, while alternatives like EPDM or EVA often rely on additives for protection. Over time, these additives can break down, reducing the material’s ability to withstand UV-related damage.
Which Option Saves More Time on Site – Cold Shrink or Heat Shrink?
Cold shrink can typically be installed in around half the time it takes to install heat shrink. The process avoids the need for hot work permits, reduces training requirements and eliminates fire-related risks. When scaled across multiple installations, this can lead to significant savings – not just in time, but also in labour, insurance and operational costs.
Follow link for more Blog Posts on: LV, MV & HV Cable Jointing, Cable Insulation and more.
