ATEX Glands and Hazardous Locations
Anyone who has been in the industry long enough knows the importance of ATEX Glands… or Hazardous Area Glands, A2EX Glands, Hazardous Glands, Hazardous Location Glands, Explosion-Proof Glands, Flame-proof Glands, Fireproof or however you want to call them!
This article will focus on identifying the science behind these polyonymous glands starting by defining the terms hazardous locations/ areas and explosive atmospheres, where special precautions are required to protect the safety of workers.
Click Here to browse around Prysmian’s ATEX Cable Glands
Definition: Hazardous Locations & Explosive Atmospheres
 In Electrical Engineering, Hazardous Locations are defined as “places where fire or explosion hazards may exist due to:
In Electrical Engineering, Hazardous Locations are defined as “places where fire or explosion hazards may exist due to:
- flammable gases,
- flammable liquid–produced vapors,
- combustible liquid–produced vapors,
- combustible dusts,
- or ignitable fibers/flyings
present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures.”
In Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmospheres Regulations (DSEAR), an Explosive Atmosphere is “a mixture of dangerous substances with air, under atmospheric conditions, in the form of gases, vapours, mist or dust in which, after ignition has occurred, combustion spreads to the entire unburned mixture”.
Components of Hazardous Areas -Elimination of one
The three components of a hazardous area, whose combination can cause an explosion are flammable substances (fuel), ignition sources (or heat) and oxidizers (air).
To make the area safe, elimination of one or more of the three elements is essential. Within an industrial application, most times it’s impossible or impractical to eliminate the flammable substance or the oxidizer.
Therefore the most practical and convenient solution is to eliminate the source of ignition.
To achieve that, the electrical equipment used and installed in such locations, should adhere to special designed and testing to ensure it does not initiate an ignition or explosion.
That’s where ATEX comes in, but… what is ATEX?
 The term ATEX derives from the French title of the 94/9/EC directive: “Appareils destinés à être utilisés en ATmosphères EXplosibles” (= equipment intented to be used in EXplosion ATmospheres).
The term ATEX derives from the French title of the 94/9/EC directive: “Appareils destinés à être utilisés en ATmosphères EXplosibles” (= equipment intented to be used in EXplosion ATmospheres).
The ATEX directive consists of two EU directives describing the equipment and work space allowed in an environment with an explosive atmosphere:
- the ATEX 95 equipment directive 94/9/EC on equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres;
- the ATEX 137 workplace directive 99/92/EC on minimum requirements for improving the safety and health protection of workers potentially at risk from explosive atmospheres.
Click Here to have a look at our ATEX Cable Glands- Hazardous Glands
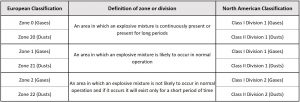
ATEX gas/ dust zone classification
The ATEX 137 Workplace Directive defines safety standards that apply to different levels of dangerous working environments. The more dangerous the environment, the more stringent the requirements. The first two zones of the following list are the most dangerous zoning classifications.
Protection Concepts
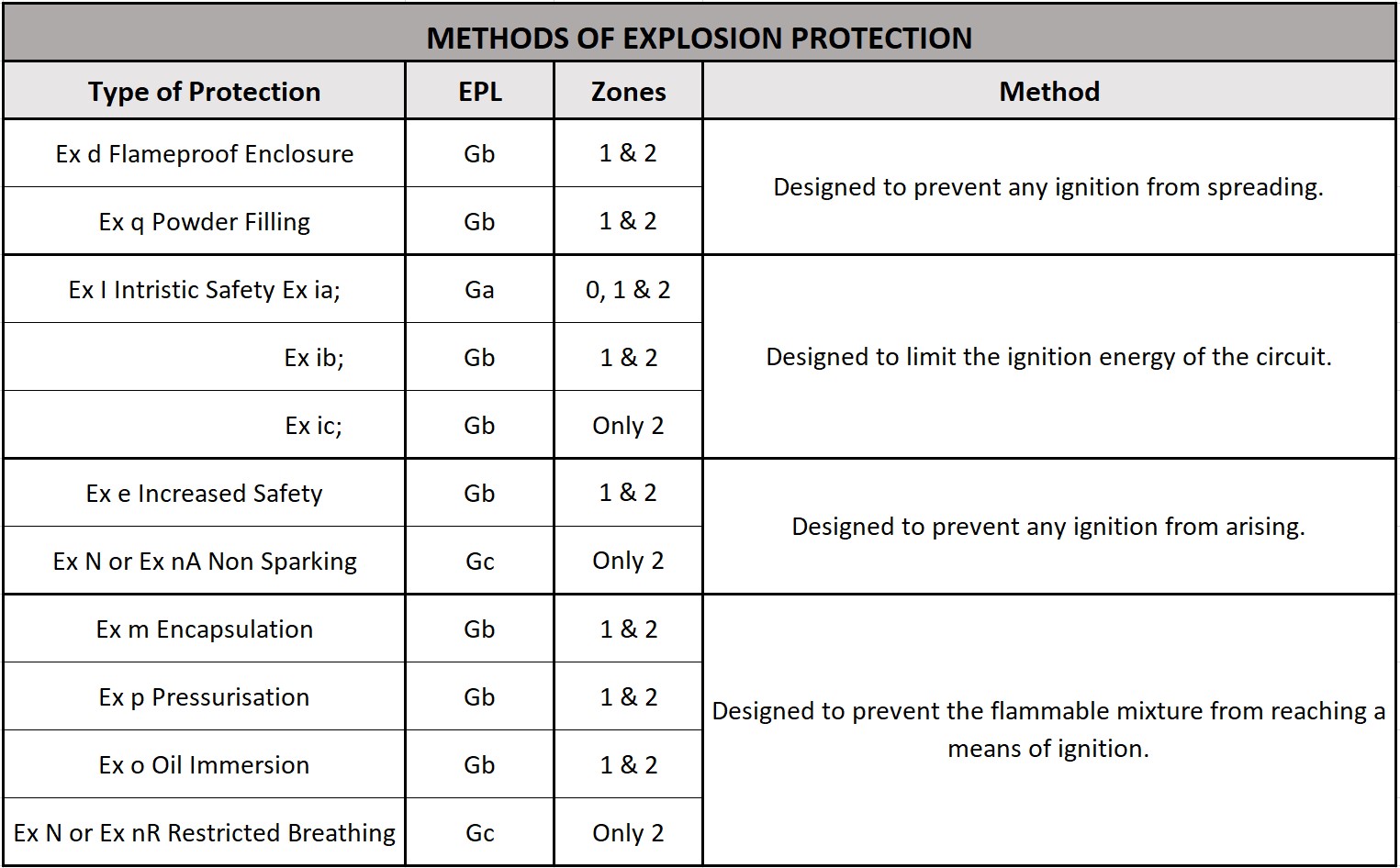
There are varying types of equipment suitable for use within these zones to ensure removal or (great reduction) of a potential explosion. Design and manufacturing of this equipment must be in accordance with particular construction parameters (protection concepts).
Essentially these concepts fall under four main methods. These methods are detailed below along with a brief description of some of the concepts:
Prysmian BICON Cable Glands
Prysmian BICON specialise in designing, engineering and manufacturing cable glands for use in explosive atmospheres. As such we have developed a dedicated range of cable glands and accessories, which protect equipment sited within areas at risk from explosion.
Their range of flameproof, explosion-proof and ATEX glands has multiple-certification. This allows customers to select one gland to cover a multitude of situations including ATEX, IECEx, cCSAus and UL.
Click Here to browse around our Prysmian BICON ATEX Cable Glands
To ensure that you choose the most suitable gland for your application consult the Cable Gland Selection Charts below:
Click Here for all Hazardous Glands
IF YOU REQUIRE ANY FURTHER ASSISTANCE, SEEK ADVICE FROM OUR TECHNICAL TEAM. THAT WAY, YOU CAN CHOOSE THE RIGHT ATEX GLANDS TO SUIT YOUR INSTALLATION!
Follow links for more Blog Posts/ Articles on: Glanding, Fire Performance, Standards & Regulations.
